Structure
The Australian Curriculum is designed to develop successful learners, confident and creative individuals, and active and informed citizens. It is presented as a progression of learning from Foundation - Year 10 that makes clear to teachers, parents, students and others in the wider community what is to be taught, and the quality of learning expected of young people as they progress through school.
The primary audience for the Australian Curriculum is teachers. The curriculum is concise and is expressed in plain language while preserving a complexity appropriate for professional practitioners. Consistency in terms of language and broad structure supports teachers in and across learning areas.
The whole curriculum
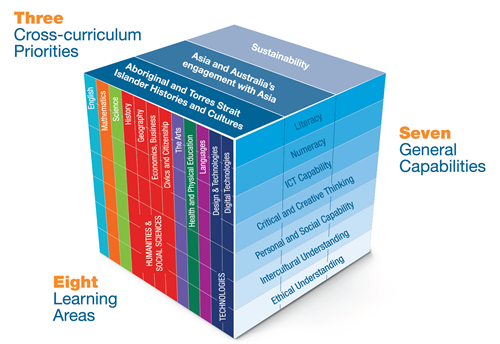
The Foundation – Year 10 Australian Curriculum is described as a three-dimensional curriculum that recognises the central importance of disciplinary knowledge, skills and understanding; general capabilities and cross-curriculum priorities.
Disciplinary knowledge is found in the eight learning areas of the Australian Curriculum: English, Mathematics, Science, Health and Physical Education, Humanities and Social Sciences, The Arts, Technologies and Languages. The latter four learning areas have been written to include multiple subjects, reflecting custom and practice in the discipline. In each learning area or subject, content descriptions specify what young people will learn; and achievement standards describe the depth of understanding and the sophistication of knowledge and skill expected of students at the end of each year level or band of years in their schooling.
Alongside disciplinary knowledge, the Australian Curriculum provides seven general capabilities: Literacy; Numeracy; Information and Communication Technology Capability; Critical and Creative Thinking; Personal and Social Capability; Ethical Understanding; and Intercultural Understanding. The general capabilities comprise an integrated and interconnected set of knowledge, skills, behaviours and dispositions that apply across subject-based content and equip students to be lifelong learners and be able to operate with confidence in a complex, information-rich, globalised world. In the Australian Curriculum, the general capabilities are developed and applied, where relevant, through the learning areas. An icon-tagging system is used to show where this can be done. General capabilities are also identified where they offer opportunities to add depth and richness to student learning via optional content elaborations. Learning continua have been developed for each capability to describe the relevant knowledge, skills, behaviours and dispositions at particular points of schooling.
The Australian Curriculum also includes three current cross-curriculum priorities that are to be developed, where relevant, through the learning areas. These are: Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Histories and Cultures; Asia and Australia’s Engagement with Asia; and Sustainability. The priorities are not separate subjects in themselves; they are addressed through learning area content, where appropriate, and identified by icons. A set of organising ideas that reflect the essential knowledge, understanding and skills has been developed for each cross-curriculum priority.
The three dimensions of the Australian Curriculum
Learning areas
The key elements of the Foundation – Year 10 Australian Curriculum learning areas or subjects are achievements standards and content descriptions. These are presented with other learning area or subject information including year-level descriptions, rationale, aims, key ideas, structure and representation of general capabilities and cross-curriculum priorities.
Achievement standards and work samples
Achievement standards for each learning area or subject describe the learning expected of students at each year level or band of years. Each achievement standard is described in two paragraphs. Typically, the first paragraph describes what students are expected to understand, and the second paragraph describes what students are expected to be able to do having been taught the curriculum content. The set of achievement standards for each learning area or subject describe a broad sequence of expected learning.
The achievement standard for each year level or band should be read as a whole (that is, the ‘understanding’ and ‘skills’ paragraphs are read together) and in the context of what is to be taught (content descriptions) for that year or band. The achievement standards provide a clear description of student learning and are, therefore, a useful starting point or driver for the development of teaching and learning programs. The achievement standard also allows teachers to monitor student learning and to make judgements about student progress and achievement. For each learning area or subject, the achievement standards are accompanied by portfolios of annotated work samples that illustrate the expected learning for each year level or band.
In addition to the subject-specific achievement standards, new learning area achievement standards have been provided for Humanities and Social Sciences, The Arts and Technologies. The default view for Technologies and The Arts is the subject-specific achievement standard; to view the learning area achievement standard select the link at the end of the achievement standard. The default view for Humanities and Social Sciences is the learning area achievement standard; to view the subject-specific achievement standard select the link at the end of the achievement standard. State and territory school and curriculum authorities determine the reporting requirements for their schools and should be consulted about whether learning area or subject-specific achievement standards are to be used for reporting.
Content descriptions and elaborations
Content descriptions describe what is to be taught and what students are expected to learn. Content descriptions include knowledge, understanding and skills, described at a year level or band of years. The content descriptions are accompanied by content elaborations, which are optional, and are provided to give teachers ideas about how they might teach the content.
Organisation and structural features of each learning area
Within the learning areas, there are many common structural and organisational features. The division of learning areas into subjects, strands, sub-strands and/or threads, which are presented as learning sequences across years or bands of schooling, ensures significant structural consistency throughout the curriculum. The combination of common structural features with one or more distinctive elements specific to a learning area ensures a learning area structure that is recognisable as the Australian Curriculum but is tailored for each particular learning area.
Year or bands of years
Each learning area or subject of the Australian Curriculum is presented as a sequence of learning (content descriptions and achievement standards) over time. The organisation varies to reflect the particular learning area including the specificity of evidence-based teaching sequence, its priority for teaching time and the need for flexibility to assist schools in planning and programming. English and Mathematics are specified at each year level from Foundation - Year 10. Some aspects of Science, Humanities and Social Sciences, and Health and Physical Education are specified at a year level; and other aspects, at two- or three-year bands. The Arts, Technologies and Languages are specified at two- or three-year bands.
Year level descriptions and/or band descriptions assist teachers by providing important information about the learning contexts that apply to the content descriptions and achievement standards at a particular year or band of years.
Learning areas, subjects, strands
The learning areas of English, Mathematics, Science, Health and Physical Education comprise a single subject. The learning areas of Humanities and Social Sciences, The Arts, Technologies and Languages each comprise multiple subjects. This reflects the custom and practice of each discipline.
Within each learning area or subject, the largest structural unit for content is a strand. Typically strands are further divided into sub-strands and/or threads, which are populated with content descriptions. The sequence of strands, sub-strands and threads from Foundation - Year 10 within each learning area or subject is most easily viewed in the scope and sequence documents, provided as PDFs, in the learning area section of the website.