In the Australian Curriculum, students develop ethical understanding as they identify and investigate the nature of ethical concepts, values and character traits, and understand how reasoning can assist ethical judgement. Ethical understanding involves students building a strong personal and socially oriented ethical outlook that helps them to manage context, conflict and uncertainty, and to develop an awareness of the influence that their values and behaviour have on others. It does this through fostering the development of ‘personal values and attributes such as honesty, resilience, empathy and respect for others’, and the capacity to act with ethical integrity, as outlined in the Melbourne Declaration on Educational Goals for Young Australians (MCEETYA 2008, p. 9).
As cultural, social, environmental and technological changes transform the world, the demands placed on learners and education systems are changing. Technologies bring local and distant communities into classrooms, exposing students to knowledge and global concerns as never before. Complex issues require responses that take account of ethical considerations such as human rights and responsibilities, animal rights, environmental issues and global justice.
Building ethical understanding throughout all stages of schooling will assist students to engage with the more complex issues that they are likely to encounter in the future, and to navigate a world of competing values, rights, interests and norms.
Students learn to develop ethical understanding as they explore ethical issues and interactions with others, discuss ideas and learn to be accountable as members of a democratic community.
Processes of inquiring into ethical issues include giving reasons, being consistent, finding meanings and causes, and providing proof and evidence. Interrogating such concepts through authentic cases such as global warming, sustainable living and socioeconomic disparity can involve group and independent inquiry, critical and creative thinking, and cooperative teamwork, and can contribute to personal and social learning.
As students engage with the elements of Ethical Understanding in an integrated way, they learn to recognise the complexity of many ethical issues. They develop a capacity to make reasoned ethical judgements through the investigation of a range of questions drawn from varied contexts in the curriculum.
![]() This icon shows where Ethical Understanding has been identified in learning area content descriptions and elaborations.
This icon shows where Ethical Understanding has been identified in learning area content descriptions and elaborations.
Key ideas
The key ideas for Ethical Understanding are organised into three interrelated elements in the learning continuum as shown in the figure below.
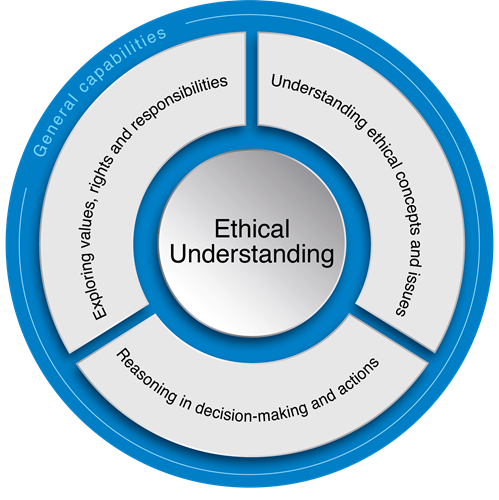
Organising elements for Ethical Understanding
This element involves students developing an understanding of ethical concepts and issues.
Students learn to recognise ethical concepts and explore ethical issues in context. They identify, examine and give examples of ethical concepts. They discuss, analyse and explore dimensions of ethical concepts in context. In developing and acting with ethical understanding, students:
- recognise ethical concepts
- explore ethical concepts in context.
This element involves students reasoning when making decisions and acting ethically.
Students consider the consequences of and reflect on ethical action. They analyse the reasoning behind stances when making ethical decisions and evaluate the intended and unintended consequences of actions in an increasing range of scenarios. Students articulate understandings of a range of ethical responses in social contexts. In developing and acting with ethical understanding, students:
- reason and make ethical decisions
- consider consequences
- reflect on ethical action.
This element involves students identifying and examining values and exploring rights and responsibilities of individuals and groups in a range of contexts and practices.
Students use instances of expressed values to explain social interactions and to determine rights and responsibilities in social and legal domains. They recognise and interpret points of view in ethical contexts. In developing and acting with ethical understanding, students:
- examine values
- explore rights and responsibilities
- consider points of view.
Ethical issues arise across all areas of the curriculum, with each learning area containing a range of content that demands consideration from an ethical perspective. This includes analysing and evaluating the ethics of the actions and motivations of individuals and groups, understanding the ethical dimensions of research and information, debating ethical dilemmas and applying ethics in a range of situations.
Students learn to develop ethical understanding as they explore ethical issues and interactions with others, discuss ideas, and learn to be accountable as members of a democratic community.
Students need regular opportunities to identify and make sense of the ethical dimensions in their learning. As ethics is largely concerned with what we ought to do and how we ought to live, students need to understand how people can inquire collaboratively and come to ethical decisions. They need the skills to explore areas of contention, select and justify an ethical position, and engage with and understand the experiences and positions of others. These skills promote students’ confidence as decision-makers and foster their ability to act with regard for others. Skills are enhanced when students have opportunities to put them into practice in their learning; for example, understanding the importance of applying appropriate ethical practices such as following the Guidelines for Ethical Research in Australian Indigenous Studies published in 2011 by the Australian Institute of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Studies (AIATSIS).Students also need to explore values, rights and responsibilities to assist them in justifying their ethical position and in engaging with the position of others.
The processes of reflecting on and interrogating core ethical issues and concepts underlie all areas of the curriculum. These include justice, right and wrong, freedom, truth, identity, empathy, goodness and abuse.
The learning area or subject with the highest proportion of content descriptions tagged with Ethical Understanding is placed first in the list.
F-6/7 Humanities and Social Sciences (HASS)
In the F–6/7 Australian Curriculum: Humanities and Social Sciences, students develop ethical understanding as they learn how to build discipline-specific knowledge about history, geography, civics and citizenship, and economics and business, as they pose questions, research, analyse, evaluate and communicate information, concepts and ideas.
Students develop ethical understanding of behaviour as they critically explore the character traits, actions and motivations of people in the past that may be the result of different standards and expectations and changing societal attitudes and values. Students recognise that examining the nature of evidence deepens their understanding of ethical issues and investigate the ways that diverse values and principles have influenced human affairs. When undertaking fieldwork, students learn about ethical procedures for investigating and working with people and places, including working with Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Peoples. When learning about the environment, students consider their responsibilities to protect other forms of life that share the environment. They evaluate their findings against the criteria of environmental protection, economic prosperity and social advancement. These criteria raise ethical questions about human rights and citizenship; for example, who bears the costs and who gains the benefits, and about group and personal responsibilities.
Students develop informed, ethical values and attitudes and become aware of their own roles, rights and responsibilities as participants in their community, their environment and the economy, and the implications of their decisions and actions for individuals, society and the environment. They discuss and apply ethical concepts such as equality, respect and fairness, which underpin Australia’s democracy, exploring values in particular contexts, such as the fairness of voting systems or particular government policies. They examine shared beliefs and values which support Australian democratic society, past and present, and the rights and responsibilities of citizenship. Students develop the skills to recognise different perspectives, and have opportunities to explore ambiguities and ethical considerations related to political, legal and social issues.
7-10 History
In the Australian Curriculum: History, students develop ethical understanding as they critically explore the character traits, actions and motivations of people in the past that may be the result of different standards and expectations and changing societal attitudes. Students recognise that examining the nature of evidence deepens their understanding of ethical issues and investigate the ways that diverse values and principles have influenced human affairs.
7-10 Geography
In the Australian Curriculum: Geography, students develop ethical understanding as they investigate current geographical issues and evaluate their findings against the criteria of environmental protection, economic prosperity and social advancement. These criteria raise ethical questions about human rights and citizenship; for example, who bears the costs and who gains the benefits, and about group and personal responsibilities. By exploring such questions, students develop informed values and attitudes and become aware of their own roles and responsibilities as citizens.
When undertaking fieldwork, students learn about ethical procedures for investigating and working with people and places, including working with Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Peoples. When thinking about the environment, students consider their responsibilities to protect other forms of life that share the environment.
7-10 Civics and Citizenship
In the Australian Curriculum: Civics and Citizenship, students discuss and apply ethical concepts such as equality, respect and fairness, which underpin Australia’s democracy. They explore and analyse democratic values in particular contexts; for example, evaluating the fairness of voting systems or particular government policies. Students explore different beliefs about civics and citizenship issues and the consequences of particular decisions. They examine shared beliefs and values which support Australian democracy and the rights and responsibilities of citizenship. Students develop the skills to recognise different perspectives and have opportunities to explore ambiguities and ethical considerations related to political, legal and social issues.
7-10 Economics and Business
In the Australian Curriculum: Economics and Business, students develop informed, ethical values and attitudes and become aware of their own roles, rights and responsibilities as participants in the economy. Students also develop an understanding of the ethical considerations that may be involved in making economics and business decisions and their implications for individuals, society and the environment.
Technologies
In the Australian Curriculum: Technologies, students develop the capacity to understand and apply ethical and socially responsible principles when collaborating with others and creating, sharing and using technologies – materials, data, processes, tools and equipment. Using an ethical lens, they investigate past, current and future local, national, regional and global technological priorities. When engaged in systems thinking, students evaluate their findings against the criteria of legality, environmental sustainability, economic viability, health, social and emotional responsibility and social awareness. They explore complex issues associated with technologies and consider possibilities. They are encouraged to develop informed values and attitudes.
Students learn about safe and ethical procedures for investigating and working with people, animals, data and materials. They consider the rights of others and their responsibilities in using sustainable practices that protect the planet and its life forms. They learn to appreciate and value the part they play in the social and natural systems in which they operate.
Students consider their own roles and responsibilities as discerning citizens, and learn to detect bias and inaccuracies. Understanding the protection of data, intellectual property and individual privacy in the school environment helps students to be ethical digital citizens.
Health and Physical Education
The Australian Curriculum: Health and Physical Education focuses on the importance of treating others with respect, integrity, fairness and compassion, and valuing diversity and equality for all.
Students examine ethical principles and codes of practice appropriate to different contexts, such as at school, at home, in the community, in relationships, on the sporting field, in the natural environment and when using digital technologies such as social media. As students explore concepts and consequences of fair play, equitable participation, empathy and respect in relationships, they develop skills to make ethical decisions and understand the consequences of their actions. They also develop the capacity to apply these skills in everyday situations and movement-based contexts.
The Arts
In the Australian Curriculum: The Arts, students develop and apply ethical understanding when they encounter or create artworks that require ethical consideration, such as work that is controversial, involves a moral dilemma or presents a biased point of view. They explore how ethical principles affect the behaviour and judgement of artists involved in issues and events. Students apply the skills of reasoning, empathy and imagination, and consider and make judgements about actions and motives. They speculate on how life experiences affect and influence people’s decision-making and whether various positions held are reasonable.
Students develop their understanding of values and ethical principles when interpreting and evaluating artworks and their meaning. They consider the intellectual, moral and property rights of others. In particular, students learn about ethical and cultural protocols when engaging with Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander Peoples and their histories, cultures and artistic practices.
Languages
When learning another language through the Australian Curriculum: Languages, students are taught explicitly to acknowledge and value difference in their interactions with others and to develop respect for diverse ways of perceiving and acting in the world. Students have opportunities to monitor and adjust their own ethical points of view. In learning Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander languages, students should consider appropriate ethical behaviour for engaging with the owners and custodians of the languages. Similar consideration is needed when interpreting and translating or when collecting and analysing primary research data.
Science
In the Australian Curriculum: Science, students develop the capacity to form and make ethical judgements in relation to experimental science, codes of practice, and the use of scientific information and science applications. They explore what integrity means in science, and explore and apply ethical guidelines in their investigations. They consider the implications of their investigations on others, the environment and living organisms.
They use scientific information to evaluate claims and to inform ethical decisions about a range of social, environmental and personal issues, for example, land use or the treatment of animals.
English
In the Australian Curriculum: English, students develop ethical understanding as they study the social, moral and ethical positions and dilemmas presented in a range of texts. They explore how ethical principles affect the behaviour and judgement of imagined characters in texts and the real-life experiences of those involved in similar issues and events. Students apply the skills of reasoning, empathy and imagination to consider and make judgements about actions and motives, and speculate on how life experiences affect and influence people’s decision-making and whether various positions held are reasonable.
Students studying the Australian Curriculum: English gradually understand how language use has inclusive and exclusive effects, as seen through the distinction between subjective language and bias, versus factual and objective language. They learn how language can be used to influence judgements about behaviour, speculate about consequences and influence opinions, and that language can carry embedded negative and positive connotations that can be used in ways that help or hurt others. Students use their growing understanding to create and express their own considered points of view on issues of empowerment and disempowerment in a range of imaginative and persuasive texts.
Mathematics
There are opportunities in the Australian Curriculum: Mathematics to explore, develop and apply ethical understanding in a range of contexts; for example, through analysing data and statistics; seeking intentional and accidental distortions; finding inappropriate comparisons and misleading scales when exploring the importance of fair comparison; and interrogating financial claims and sources.
Work Studies
In the Australian Curriculum: Work Studies, Years 9–10, students learn how ethical understanding focuses on the importance of treating others with honesty, integrity, consideration, compassion and respect. Students are given opportunities to explore moral principles and codes of practice appropriate to different contexts such as in building relationships at school, in the workplace and in the broader community, and to develop the commitment and capacity to be consistently guided by these principles.